|
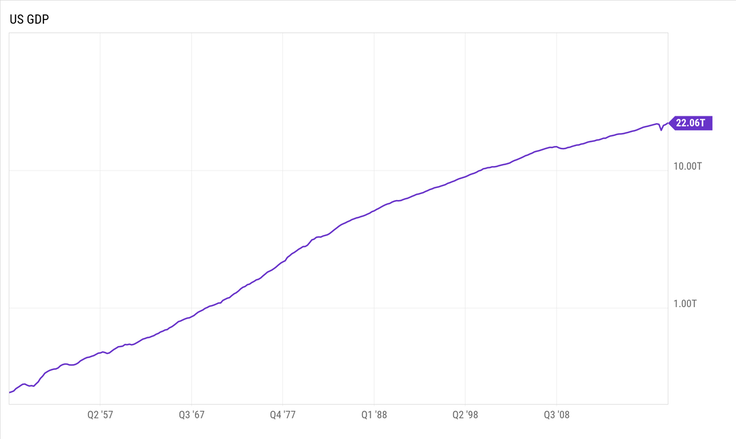
Why is GDP So Closely Watched and So Important to Economists, Policy Makers, and Investors? Plain and simple, it's an important way to determine how well a country’s economy is doing. Because GDP is closely watched by so many different people, organizations, and governments around the world, it’s important to understand exactly what it is, how it’s calculated, and what it’s used for. What exactly is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)? Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the dollar value of all final economic goods and services produced in a country during a specific period of time. It is the broadest financial measurement of a nation’s total economic activity. This includes all the goods and services bought by individuals, government spending, investments, and net exports. In a nutshell it’s the value of all the goods and services produced in the United States. The percentage that GDP grew (or shrank) from one period to another is an important way for people to gauge how the economy is doing. Due to the size of the United States economy, the U.S. GDP is closely watched around the world as an economic barometer. GDP is calculated and produced by the BEA (Bureau of Economic Analysis) which measure the value and makeup of the nation's output, the types of income generated, and how that income is used. The most common way GDP is calculated is using the Expenditure Approach, which is based on the money spent by various groups. GDP = C + G + I + NX where: C = Consumption or all private consumer spending within a country’s economy, including, durable goods (items with a lifespan greater than three years), non-durable goods (food & clothing), and services. G = Government expenditures, including salaries of government employees, road construction/repair, public schools, and military expenditure. I = Investments spent on capital equipment, inventories, and housing. NX = Net Exports (country’s total exports - total imports). What are the various ways GDP is adjusted? GPD can be measured in several different ways. Some of the most common are: Nominal GDP – The total value of all goods and services produced at current market prices. This includes all the changes in market prices during the current year due to inflation or deflation. Real GDP – The sum of all goods and services produced at constant prices. The prices used in determining the Gross Domestic Product are based on a certain base year or the previous year. This provides a more accurate account of economic growth, as it is already an inflation-adjusted measurement, meaning the effects of inflation are taken out. Actual GDP – Real-time measurement of all outputs at any interval or any given time. It demonstrates the existing state of business of the economy. Potential GDP – Ideal economic condition with 100% employment across all sectors, steady currency, and stable product prices. The United States GDP most recently passed over 22 trillion dollars, the highest level ever recorded.
Most often, the number you'll hear people refer to as "GDP" is as a percentage. That's the rate of change in real GDP from the previous quarter or year. One way to determine how well a country’s economy is doing, is by its GDP growth rate. This rate reflects the increase or decrease in the percentage of economic output in monthly, quarterly, or yearly periods. GDP data compiled by the BEA is often seasonally adjusted to remove the effects of yearly patterns, such as winter weather, holidays, or factory production schedules, which helps reflect the true patterns in economic activity. The BEA also releases GDP data that are not seasonally adjusted. Why is Measuring GDP So Important? Government officials, investors, and business people can answer questions like: How fast is the U.S. economy growing? Which industries are growing? Which are slowing? How can tweak spending and taxing to improve GDP? The White House, Congress, the Federal Reserve and other government agencies use GDP numbers to plan spending and tax policy. The Federal Reserve uses them when setting monetary policy. State and local governments rely on GDP numbers for planning purposes. Businesses use GDP and other information to help them when making decisions about jobs, expansion, investments, etc. Gross Domestic Product enables economic policymakers to assess whether the economy is weakening or progressing, if it needs improvements or restrictions, and if threats of recession or inflation are imminent. From these assessments, government agencies can determine if expansionary, monetary policies are needed to address economic issues. As a quick example: The mortgage rate you pay on your home is based upon the 10-year Treasury rate, and the 10-year Treasury rate is affected by the short-term interest rate that is set by the Federal Reserve which is using GDP numbers (as well as other information) to determine their course of action. Investors place importance on GDP growth rates to decide how the economy is changing so that they can make potentially make adjustments to their asset allocation, savings rates, and spending. When there is an economic slump, businesses experience low profits, which can mean consumers tend to cut spending. Investors are also on the lookout for potential investments, locally and abroad, basing their judgment on countries’ growth rate comparisons. So there you go, the next time you hear the GDP number in the news, you’ll know what it is, how it’s calculated and why it’s important. -Paul R. Rossi, CFA Link here to 2-page printable explainer "What is GDP?"
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |